Everyone around is talking about the dreaded Nipah Virus and how it is endangering the lives of people and healthcare professionals in remote parts of Kerala. What is this Nipah virus? Where did this suddenly come from? Can it be treated? Let’s find out.
[the_ad id=”1146″]
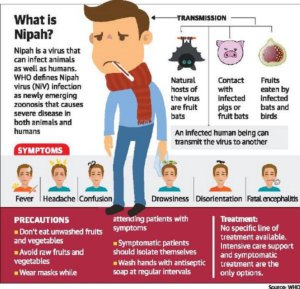
Basic facts you should know about Nipah virus:
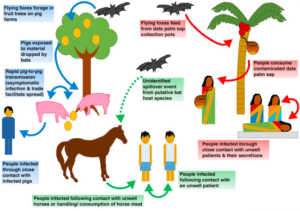
- First discovered in Malaysia and Singapore in 1998 when a large number of pigs and humans handling them were massively infected. The number of deaths reported shot up and people across the world took notice.
- The Nipah virus was first identified as a zoonotic pathogen- spreading from animals to humans and later from humans to humans as well.
- In the Bangladesh and India, when reports of the disease appeared, it was known to have been caused by the consumption of fruits or fruit products (e.g. raw date palm juice) contaminated with urine or saliva from infected fruit bats.
- The initial symptoms start off with a mild fever, headache, nausea and progress onto vomiting, dizziness, disorientation, confusion, encephalitis, pulmonary illness and resulting in coma and death.
- The time gap between the infection and the onset of symptoms is usually 4-15 days.
- Laboratory tests to confirm the presence of the Nipah virus include real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) from bodily fluids as well as antibody detection via ELISA, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay and virus isolation by cell culture.
- Currently, there is no vaccine or treat Nipah virus and the only treatment option available is supportive care.
Also read: The importance of nurses in health care
Pic courtesy: timesofindia
How to reduce the risk of infection of Nipah virus?
- Since there is no preventive treatment, a basic awareness on the possible routes of infection should be made among the general public.
- Freshly collected date palm juice should be boiled and fruits should be thoroughly washed and peeled before consumption to reduce the risk of bat-to-human transmission.
- Avoid contact with infected pigs. For healthcare providers, make sure you wear the right gloves and masks to keep yourself well protected.
- Insist on proper handwashing practices for everyone in the family and also don’t forget to wash the fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
Pic courtesy: emitpost
