Monoclonal antibodies-based treatment of cancer has been established as one of the most successful therapeutic strategies for both hematologic malignancies and solid tumours in the last 20 years. Targeted drug therapies are being developed to specifically attack cancer cells than traditional, toxic chemotherapy drugs.
Understanding the genetics of cancer
The beginning of Monoclonal antibodies:
First generated in mice in 1975 using a hybridoma technique, Georges Kohler and Cesar Milstein shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1984. The initial combining of serological techniques for cancer cell surface antigen and discovery with hybridoma technology led to a series of landmark clinical trials that paved the way for new generation antibodies against Tumour surface antigen Specific for tumours like, CD Antigen 20 for NHL, CEA for Colorectal ca Growth factor Her2 for CA breast. The first licenced monoclonal antibody was Orthoclone OKT3.
Monoclonal antibody have suffix or stem and these class of drugs have name end as “ mab” , “nib” , “nab” or “mib”.
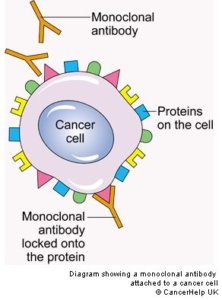
Pic courtesy: cancerresearchuk.org
Diabetic Foot Syndrome- what it means to the medical student
What do they denote?
1. The names ending in “mab”.
MAB are antibodies engineered in the laboratory, to bind to specific antigens on the surfaces of tumour cells. They may induce an immunological response against cancer cells.
2. The names ending in “nib”
NIB has the suffix “nib”, that indicates a small-molecule inhibitor of kinase enzymes. They are as follows:
“tinib” is used for tyrosine kinase inhibitors
“anib” for angiogenesis inhibitors
“rafenib” for RAF kinase inhibitors
“alectinib” for advanced non-small cell lung cancer
“cobimetinib”for advanced melanoma
“lenvatinib” for advanced thyroid cancer
“osimertinib” for non-small cell lung cancer
3. The names ending in “mib”
MIB is the suffix for protease or proteasome inhibitors. Mibs are small molecules that work inside cancer cells to slow proliferation and increase apoptosis. Proteasomes are enzymes found in cells which participate in regulating cell function and growth. The inhibition of these enzymes can lead to the death of cancer cells. Bortezomib and Ixazomib for multiple myeloma.
4. The names ending in “nab”
NAB is Nanoparticle albumin-bound, “nab” technology, attaching cytotoxic drugs to albumin and kill cancer cells.
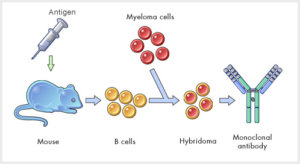
Pic courtesy: kyowa-kirin.com
MAB – Monoclonal antibody
Monoclonal antibodies are molecular engineered products that attack cancer cells by a variety of immunological mechanisms.
Most targeted therapies are either small molecules or monoclonal antibodies. Small-molecule compounds are typically developed for targets that are located inside the cell because of their ability to enter cells relatively easily. Monoclonal antibodies are relatively large and are used for targets that are outside cells or on the cell surface.
Before monoclonal antibodies are used in humans, they are “humanised” by replacing as much of the mouse antibody molecule as possible with corresponding portions of human antibodies. Some of the common MAB s used are,
Adenocarcinoma of the stomach Trastuzumab
Bladder cancer Atezolizumab
Brain cancer Bevacizumab
Breast cancer Trastuzumab
Cervical cancer Bevacizumab
Giant cell tumor of the bone Denosumab
RCC Kidney Bevacizumab
Lymphoma Ibritumomab tiuxetan
Names for monoclonal antibodies, use stems. These include prefixes, suffixes, and other indicators. Source identifiers are used as infixes preceding the -mab
-umab (human)
-omab (mouse)
-ximab (chimera)
-zumab (humanized)
| Drug Name | PREFIX | INFIX | SUFFIX | |
| MCA
| ||||
| CETUXIMAB | Cetu | xi | Mab | Infix XI denotes chimeric in origin |
| TRASTUZUMAB | Trastu | zu | Mab | Infix ZU denotes humanized in origin |
| ADAIMUMAB | Adai | mu | Mab | Infix U denotes human in origin |
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) inhibits or blocks the enzyme tyrosine kinase. The study of DNA, the cell cycle, and molecular signalling pathways paved way for the development of TKIs. Growth factors like EGF, PDGF, VEGFR are involved in the initialization and regulation of cell cycles.
Imatinib blocks a kinase receptor from binding to ATP, preventing the phosphorylation. Gefinitib inhibits EGFR. Sorafenib acts on kinase signalling cascade. Nilotinib inhibits the fusion protein
| Tyrosine kinase Inhibitor | |||
| IMATINIB | tinib | ||
| LENVATINIB | tinib | ||
| ERLOTINIB | tinib |
